Electronics |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › Electronic Arts翻译 › Electronics |
Electronics
|
Journals
Active Journals
Find a Journal
Proceedings Series
Topics
Information
For Authors
For Reviewers
For Editors
For Librarians
For Publishers
For Societies
For Conference Organizers
Open Access Policy
Institutional Open Access Program
Special Issues Guidelines
Editorial Process
Research and Publication Ethics
Article Processing Charges
Awards
Testimonials
Author Services
Initiatives
Sciforum
MDPI Books
Preprints.org
Scilit
SciProfiles
Encyclopedia
JAMS
Proceedings Series
About
Overview
Contact
Careers
News
Press
Blog
Sign In / Sign Up
Notice
clear
Notice
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader. Continue Cancel clearAll articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess. Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications. Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers. Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.  Journals
Active Journals
Find a Journal
Proceedings Series
Topics
Information
For Authors
For Reviewers
For Editors
For Librarians
For Publishers
For Societies
For Conference Organizers
Open Access Policy
Institutional Open Access Program
Special Issues Guidelines
Editorial Process
Research and Publication Ethics
Article Processing Charges
Awards
Testimonials
Author Services
Initiatives
Sciforum
MDPI Books
Preprints.org
Scilit
SciProfiles
Encyclopedia
JAMS
Proceedings Series
About
Overview
Contact
Careers
News
Press
Blog
Sign In / Sign Up
Submit
Journals
Active Journals
Find a Journal
Proceedings Series
Topics
Information
For Authors
For Reviewers
For Editors
For Librarians
For Publishers
For Societies
For Conference Organizers
Open Access Policy
Institutional Open Access Program
Special Issues Guidelines
Editorial Process
Research and Publication Ethics
Article Processing Charges
Awards
Testimonials
Author Services
Initiatives
Sciforum
MDPI Books
Preprints.org
Scilit
SciProfiles
Encyclopedia
JAMS
Proceedings Series
About
Overview
Contact
Careers
News
Press
Blog
Sign In / Sign Up
Submit
 4.7
4.7
 2.9
Journals
Electronics
2.9
Journals
Electronics
 AI-Based Real-Time Star Tracker
AI-Based Real-Time Star Tracker
 Blockchain-Enabled IoT for Rural Healthcare: Hybrid-Channel Communication with Digital Twinning
Blockchain-Enabled IoT for Rural Healthcare: Hybrid-Channel Communication with Digital Twinning
 Two Functional Wheel Mechanism Capable of Step Ascending for Personal Mobility Aids
Two Functional Wheel Mechanism Capable of Step Ascending for Personal Mobility Aids
 Temporary Bonding and Debonding in Advanced Packaging: Recent Progress and Applications
Temporary Bonding and Debonding in Advanced Packaging: Recent Progress and Applications
 Research and Development Review of Power Converter Topologies and Control Technology for Electric Vehicle Fast-Charging Systems
Journal Description
Electronics
Electronics
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on the science of electronics and its applications published semimonthly online by MDPI. The Polish Society of Applied Electromagnetics (PTZE) is affiliated with Electronics and their members receive a discount on article processing charges.
Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), CAPlus / SciFinder, Inspec, and other databases.
Journal Rank: JCR - Q2(Electrical and Electronic Engineering) CiteScore - Q2 (Electrical and Electronic Engineering)
Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first
decision is provided to authors approximately 15.8 days after submission; acceptance
to publication is undertaken in 2.7 days (median values for papers published in
this journal in the first half of 2023).
Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Companion journals for Electronics include: Magnetism, Signals, Network and Software.
Impact Factor:
2.9 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.9 (2022)
subject
Imprint Information
get_app
Journal Flyer
Open Access
ISSN: 2079-9292
Latest Articles
get_app
Open AccessArticle
Collaborative Mixture-of-Experts Model for Multi-Domain Fake News Detection
by
Research and Development Review of Power Converter Topologies and Control Technology for Electric Vehicle Fast-Charging Systems
Journal Description
Electronics
Electronics
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on the science of electronics and its applications published semimonthly online by MDPI. The Polish Society of Applied Electromagnetics (PTZE) is affiliated with Electronics and their members receive a discount on article processing charges.
Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), CAPlus / SciFinder, Inspec, and other databases.
Journal Rank: JCR - Q2(Electrical and Electronic Engineering) CiteScore - Q2 (Electrical and Electronic Engineering)
Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first
decision is provided to authors approximately 15.8 days after submission; acceptance
to publication is undertaken in 2.7 days (median values for papers published in
this journal in the first half of 2023).
Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Companion journals for Electronics include: Magnetism, Signals, Network and Software.
Impact Factor:
2.9 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.9 (2022)
subject
Imprint Information
get_app
Journal Flyer
Open Access
ISSN: 2079-9292
Latest Articles
get_app
Open AccessArticle
Collaborative Mixture-of-Experts Model for Multi-Domain Fake News Detection
by
 Jian Zhao, Jian Zhao,  Zisong Zhao, Zisong Zhao,  Lijuan Shi, Lijuan Shi,  Zhejun Kuang and Zhejun Kuang and  Yazhou Liu
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3440; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163440 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
With the widespread popularity of online social media, people have come to increasingly rely on it as an information and news source. However, the growing spread of fake news on the Internet has become a serious threat to cyberspace and society at large.
[...] Read more.
With the widespread popularity of online social media, people have come to increasingly rely on it as an information and news source. However, the growing spread of fake news on the Internet has become a serious threat to cyberspace and society at large. Although a series of previous works have proposed various methods for the detection of fake news, most of these methods focus on single-domain fake-news detection, resulting in poor detection performance when considering real-world fake news with diverse news topics. Furthermore, any news content may belong to multiple domains. Therefore, detecting multi-domain fake news remains a challenging problem. In this study, we propose a multi-domain fake-news detection framework based on a mixture-of-experts model. The input text is fed to BertTokenizer and embeddings are obtained by jointly calling CLIP to obtain the fusion features. This avoids the introduction of noise and redundant features during feature fusion. We also propose a collaboration module, in which a sentiment module is used to analyze the inherent sentimental information of the text, and sentence-level and domain embeddings are used to form the collaboration module. This module can adaptively determine the weights of the expert models. Finally, the mixture-of-experts model, composed of TextCNN, is used to learn the features and construct a high-performance fake-news detection model. We conduct extensive experiments on the Weibo21 dataset, the results of which indicate that our multi-domain methods perform well, in comparison with baseline methods, on the Weibo21 dataset. Our proposed framework presents greatly improved multi-domain fake-news detection performance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Computer Science & Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures Yazhou Liu
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3440; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163440 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
With the widespread popularity of online social media, people have come to increasingly rely on it as an information and news source. However, the growing spread of fake news on the Internet has become a serious threat to cyberspace and society at large.
[...] Read more.
With the widespread popularity of online social media, people have come to increasingly rely on it as an information and news source. However, the growing spread of fake news on the Internet has become a serious threat to cyberspace and society at large. Although a series of previous works have proposed various methods for the detection of fake news, most of these methods focus on single-domain fake-news detection, resulting in poor detection performance when considering real-world fake news with diverse news topics. Furthermore, any news content may belong to multiple domains. Therefore, detecting multi-domain fake news remains a challenging problem. In this study, we propose a multi-domain fake-news detection framework based on a mixture-of-experts model. The input text is fed to BertTokenizer and embeddings are obtained by jointly calling CLIP to obtain the fusion features. This avoids the introduction of noise and redundant features during feature fusion. We also propose a collaboration module, in which a sentiment module is used to analyze the inherent sentimental information of the text, and sentence-level and domain embeddings are used to form the collaboration module. This module can adaptively determine the weights of the expert models. Finally, the mixture-of-experts model, composed of TextCNN, is used to learn the features and construct a high-performance fake-news detection model. We conduct extensive experiments on the Weibo21 dataset, the results of which indicate that our multi-domain methods perform well, in comparison with baseline methods, on the Weibo21 dataset. Our proposed framework presents greatly improved multi-domain fake-news detection performance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Computer Science & Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle Impact Mechanisms of Commutation Failure Caused by a Sending-End AC Fault and Its Recovery Speed on Transient Stability by Yifeng Lin, Yifeng Lin,  Jiawei Hu, Jiawei Hu,  Tong Wang and Tong Wang and  Zengping Wang
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3439; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163439 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
A sending-end AC fault may lead to commutation failure (CF) in a line-commutated converter high-voltage direct current (LCC-HVDC) system. In this paper, a theoretical analysis of the impact mechanisms of a CF and its recovery speed on the transient stability of a sending-end
[...] Read more.
A sending-end AC fault may lead to commutation failure (CF) in a line-commutated converter high-voltage direct current (LCC-HVDC) system. In this paper, a theoretical analysis of the impact mechanisms of a CF and its recovery speed on the transient stability of a sending-end power system (TSSPS) is performed. Firstly, the models of the sending-end power system and DC power of CF are established; the ramp function is utilized to characterize the DC power recovery process. Secondly, the swing direction of the relative rotor angle caused by a sending-end AC fault is discussed, and the DC power flow method is employed to theoretically analyze the impacts of CF and its recovery speed on TSSPS. Next, the mathematic relations between parameters of the voltage-dependent current order limiter (VDCOL) and DC power recovery speed are further derived. It is concluded that the impacts of CF and its recovery speed on transient stability are related to the swing direction caused by a sending-end AC fault, the inertia of generators, and the location of the rectifier station. Finally, the theoretical analysis is validated by Kundur’s two-area system and IEEE 68-bus-based AC/DC asynchronous interconnection test power systems, respectively.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Power System Dynamics and Stability)
►▼
Show Figures Zengping Wang
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3439; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163439 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
A sending-end AC fault may lead to commutation failure (CF) in a line-commutated converter high-voltage direct current (LCC-HVDC) system. In this paper, a theoretical analysis of the impact mechanisms of a CF and its recovery speed on the transient stability of a sending-end
[...] Read more.
A sending-end AC fault may lead to commutation failure (CF) in a line-commutated converter high-voltage direct current (LCC-HVDC) system. In this paper, a theoretical analysis of the impact mechanisms of a CF and its recovery speed on the transient stability of a sending-end power system (TSSPS) is performed. Firstly, the models of the sending-end power system and DC power of CF are established; the ramp function is utilized to characterize the DC power recovery process. Secondly, the swing direction of the relative rotor angle caused by a sending-end AC fault is discussed, and the DC power flow method is employed to theoretically analyze the impacts of CF and its recovery speed on TSSPS. Next, the mathematic relations between parameters of the voltage-dependent current order limiter (VDCOL) and DC power recovery speed are further derived. It is concluded that the impacts of CF and its recovery speed on transient stability are related to the swing direction caused by a sending-end AC fault, the inertia of generators, and the location of the rectifier station. Finally, the theoretical analysis is validated by Kundur’s two-area system and IEEE 68-bus-based AC/DC asynchronous interconnection test power systems, respectively.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Power System Dynamics and Stability)
►▼
Show Figures
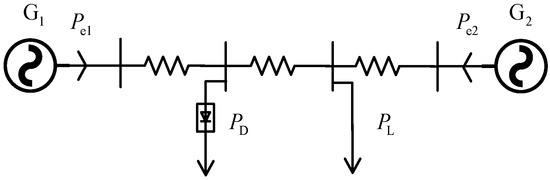 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle Joint Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Location and Beamforming and Caching Optimization for Cache-Enabled Multi-Unmanned-Aerial-Vehicle Networks by Zikang Chen, Zikang Chen,  Ming Zeng and Ming Zeng and  Zesong Fei
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3438; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163438 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
Due to the advantages such as high flexibility, low cost and easy implementation offered by unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), a UAV-assisted network is regard as an appealing solution to a seamless coverage, high disaster-tolerant and on-demand wireless system. In this paper, we focus
[...] Read more.
Due to the advantages such as high flexibility, low cost and easy implementation offered by unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), a UAV-assisted network is regard as an appealing solution to a seamless coverage, high disaster-tolerant and on-demand wireless system. In this paper, we focus on the downlink transmission in a cache-enabled UAV-assisted wireless communication network, where UAVs cache popular content from a macro base station in advance and cooperatively transfer the content to users. We aim to minimize the average transmission latency of the system and to formulate an optimization problem that jointly optimizes the UAV location, beamforming and caching strategy. However, the formulated problem is very challenging because of its non-convexity and the highly coupled optimization variables. To solve this resulting problem efficiently, we decompose it into two subproblems, namely UAV location and beamforming optimization, and UAV caching strategy optimization. The first subproblem is an NP-hard joint optimization problem, while the second one is a linear programing problem. By adopting the first-order Taylor expansion, we propose a convex optimization algorithm based on the difference-of-convex (DC) method. Specifically, we bring out a method to apply linear approximation in the DC-based algorithm, which is particularly suitable to the problems involving complicated summations. The numerical results demonstrate that the proposed DC-based iterative optimization algorithm can efficiently reduce the average transmission latency of the system.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures Zesong Fei
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3438; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163438 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
Due to the advantages such as high flexibility, low cost and easy implementation offered by unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), a UAV-assisted network is regard as an appealing solution to a seamless coverage, high disaster-tolerant and on-demand wireless system. In this paper, we focus
[...] Read more.
Due to the advantages such as high flexibility, low cost and easy implementation offered by unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), a UAV-assisted network is regard as an appealing solution to a seamless coverage, high disaster-tolerant and on-demand wireless system. In this paper, we focus on the downlink transmission in a cache-enabled UAV-assisted wireless communication network, where UAVs cache popular content from a macro base station in advance and cooperatively transfer the content to users. We aim to minimize the average transmission latency of the system and to formulate an optimization problem that jointly optimizes the UAV location, beamforming and caching strategy. However, the formulated problem is very challenging because of its non-convexity and the highly coupled optimization variables. To solve this resulting problem efficiently, we decompose it into two subproblems, namely UAV location and beamforming optimization, and UAV caching strategy optimization. The first subproblem is an NP-hard joint optimization problem, while the second one is a linear programing problem. By adopting the first-order Taylor expansion, we propose a convex optimization algorithm based on the difference-of-convex (DC) method. Specifically, we bring out a method to apply linear approximation in the DC-based algorithm, which is particularly suitable to the problems involving complicated summations. The numerical results demonstrate that the proposed DC-based iterative optimization algorithm can efficiently reduce the average transmission latency of the system.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle Adaptive Absolute Attitude Determination Algorithm for a Fine Guidance Sensor by Yuanyu Yang, Yuanyu Yang,  Chenyan Fang, Chenyan Fang,  Quan Zhang and Quan Zhang and  Dayi Yin
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3437; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163437 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
In order to ensure the attitude determination accuracy and speed of a fine guidance sensor (FGS) in a space telescope with limited onboard hardware computing resources, an adaptive absolute attitude determination algorithm was proposed. The more stars involved in the attitude determination, the
[...] Read more.
In order to ensure the attitude determination accuracy and speed of a fine guidance sensor (FGS) in a space telescope with limited onboard hardware computing resources, an adaptive absolute attitude determination algorithm was proposed. The more stars involved in the attitude determination, the higher the attitude accuracy, but more hardware resources will be consumed. By analyzing the relationship between the attitude determination accuracy and the number of stars (NOS) in the field of view (FOV), and the relationship between the detector exposure time and the NOS, an adaptive method of adjusting the NOS in the FOV was proposed to keep the number of observed stars in the FOV of the detector at a target value. The star map recognition algorithm based on improved log-polar transformation has a higher recognition speed than the traditional algorithm but cannot accurately identify and match the corresponding guide star when the number of observed stars is less than the number of guide stars. Thus, a comparison-AND star identification algorithm based on polar coordinates was proposed. In the case of a given line-of-sight pointing and 100-frame image simulation calculation, the root mean square (RMS) value of the line-of-sight pointing error was less than 37 mas in the direction of a right ascension, and less than 25 mas in the direction of declination, as concluded from the experimental simulation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures Dayi Yin
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3437; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163437 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
In order to ensure the attitude determination accuracy and speed of a fine guidance sensor (FGS) in a space telescope with limited onboard hardware computing resources, an adaptive absolute attitude determination algorithm was proposed. The more stars involved in the attitude determination, the
[...] Read more.
In order to ensure the attitude determination accuracy and speed of a fine guidance sensor (FGS) in a space telescope with limited onboard hardware computing resources, an adaptive absolute attitude determination algorithm was proposed. The more stars involved in the attitude determination, the higher the attitude accuracy, but more hardware resources will be consumed. By analyzing the relationship between the attitude determination accuracy and the number of stars (NOS) in the field of view (FOV), and the relationship between the detector exposure time and the NOS, an adaptive method of adjusting the NOS in the FOV was proposed to keep the number of observed stars in the FOV of the detector at a target value. The star map recognition algorithm based on improved log-polar transformation has a higher recognition speed than the traditional algorithm but cannot accurately identify and match the corresponding guide star when the number of observed stars is less than the number of guide stars. Thus, a comparison-AND star identification algorithm based on polar coordinates was proposed. In the case of a given line-of-sight pointing and 100-frame image simulation calculation, the root mean square (RMS) value of the line-of-sight pointing error was less than 37 mas in the direction of a right ascension, and less than 25 mas in the direction of declination, as concluded from the experimental simulation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle Development of a Compliant Lower-Limb Rehabilitation Robot Using Underactuated Mechanism by Yunlong Yang, Yunlong Yang,  Junlong Guo, Junlong Guo,  Yufeng Yao and Yufeng Yao and  Hesheng Yin
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3436; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163436 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
Most existing lower-limb rehabilitation robots (LLRR) for stroke and postoperative rehabilitation are bulky and prone to misalignments between robot and human joints. These drawbacks hamper LLRR application, leading to poor arthro-kinematic compatibility. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a novel robot with
[...] Read more.
Most existing lower-limb rehabilitation robots (LLRR) for stroke and postoperative rehabilitation are bulky and prone to misalignments between robot and human joints. These drawbacks hamper LLRR application, leading to poor arthro-kinematic compatibility. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a novel robot with portability and compliance features. The developed robot consists of an underactuated mechanism and a crus linkage, respectively corresponding to the hip and knee joints. The underactuated mechanism is a new type of remote center of motion (RCM) mechanism with two sets of contractible slider cranks that can reduce the misalignments between robot and human joints. The underactuated mechanism is then optimized using the particle swarm optimization method, and the developed robot’s kinematic analysis is presented. The proposed robot can be simplified as a two-link mechanism with the ability to easily plan its trajectory using the modified Denavit–Hartenberg method. Finally, passive exercise trials demonstrate that the mismatch angles between the human and robot knee joints are less than 2.1% of the range of motion, confirming the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed robot.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Wearable/Flexible Devices and Systems in Bioelectronics)
►▼
Show Figures Hesheng Yin
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3436; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163436 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
Most existing lower-limb rehabilitation robots (LLRR) for stroke and postoperative rehabilitation are bulky and prone to misalignments between robot and human joints. These drawbacks hamper LLRR application, leading to poor arthro-kinematic compatibility. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a novel robot with
[...] Read more.
Most existing lower-limb rehabilitation robots (LLRR) for stroke and postoperative rehabilitation are bulky and prone to misalignments between robot and human joints. These drawbacks hamper LLRR application, leading to poor arthro-kinematic compatibility. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a novel robot with portability and compliance features. The developed robot consists of an underactuated mechanism and a crus linkage, respectively corresponding to the hip and knee joints. The underactuated mechanism is a new type of remote center of motion (RCM) mechanism with two sets of contractible slider cranks that can reduce the misalignments between robot and human joints. The underactuated mechanism is then optimized using the particle swarm optimization method, and the developed robot’s kinematic analysis is presented. The proposed robot can be simplified as a two-link mechanism with the ability to easily plan its trajectory using the modified Denavit–Hartenberg method. Finally, passive exercise trials demonstrate that the mismatch angles between the human and robot knee joints are less than 2.1% of the range of motion, confirming the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed robot.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Wearable/Flexible Devices and Systems in Bioelectronics)
►▼
Show Figures
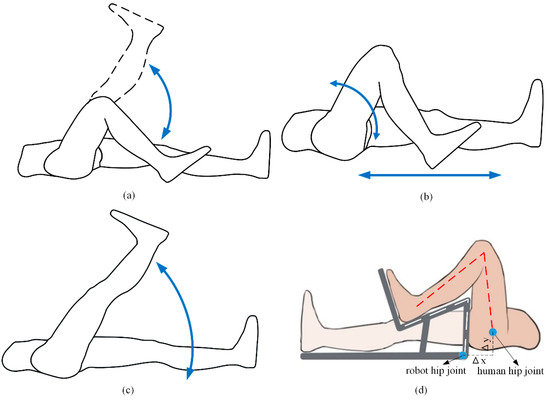 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle Handover Triggering Prediction with the Two-Step XGBOOST Ensemble Algorithm for Conditional Handover in Non-Terrestrial Networks by Eunsu Kim and Eunsu Kim and  Inwhee Joe
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3435; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163435 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
A Non-Terrestrial Network (NTN) is a network system that enables service for areas where terrestrial networks cannot cover. An NTN provides communication services using flying objects such as UAVs, HAPs, and satellites. In the case of satellites, they move in Earth’s orbit at
[...] Read more.
A Non-Terrestrial Network (NTN) is a network system that enables service for areas where terrestrial networks cannot cover. An NTN provides communication services using flying objects such as UAVs, HAPs, and satellites. In the case of satellites, they move in Earth’s orbit at a constant speed. Ground services from continuously moving satellites cause frequent handovers. In addition, frequent handovers may come as a load between User Equipment (UE) and the communication system, which leads to degradation of service quality. Unlike Terrestrial Networks (TN), communication services are provided to UEs at altitudes ranging from 20 km to 35,584 km, rather than from base stations close to the ground. Service at high altitudes is unreliable due to the measurement values that were previously used as quality indicators to operate terrestrial networks. Moreover, service at high altitudes demands long-distance communication, and propagation delay occurs from the long-distance communication. In the 3GPP Rel. 17 document, it is suggested that the above problems should be solved. This paper tries to solve the problem by proposing the two-step XGBOOST, a CART-based Gradient Boosting Model. Handover in TN uses measurement-based conditional handover (CHO), but the measured values in the NTN environment are not valid. Using this, the distance between the UE and the center of the cell and the elevation angle are used to construct a model that predicts the HO triggering time point. In order to overcome the propagation delay caused by communication at a high altitude, a model that predicts the distance and elevation angle between the UE and the center of the cell considering the propagation delay is proposed. The model is composed of two-step XGBOOST. The one-step model is a model in which the UE predicts the distance and elevation angle between cell centers after propagation delay at the time when satellite position information is transmitted to the UE. The two-step model predicts handover triggering occurrence based on the data predicted by the one-step result. As a result of the experiment, the model considering the propagation delay showed about 8% better performance on average than the model not considering the propagation delay, and the XGBOOST model achieved an average F1-score of 0.9891 in the propagation delay experiments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Optimization and Machine Learning for Wireless Communications)
►▼
Show Figures Inwhee Joe
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3435; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163435 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
A Non-Terrestrial Network (NTN) is a network system that enables service for areas where terrestrial networks cannot cover. An NTN provides communication services using flying objects such as UAVs, HAPs, and satellites. In the case of satellites, they move in Earth’s orbit at
[...] Read more.
A Non-Terrestrial Network (NTN) is a network system that enables service for areas where terrestrial networks cannot cover. An NTN provides communication services using flying objects such as UAVs, HAPs, and satellites. In the case of satellites, they move in Earth’s orbit at a constant speed. Ground services from continuously moving satellites cause frequent handovers. In addition, frequent handovers may come as a load between User Equipment (UE) and the communication system, which leads to degradation of service quality. Unlike Terrestrial Networks (TN), communication services are provided to UEs at altitudes ranging from 20 km to 35,584 km, rather than from base stations close to the ground. Service at high altitudes is unreliable due to the measurement values that were previously used as quality indicators to operate terrestrial networks. Moreover, service at high altitudes demands long-distance communication, and propagation delay occurs from the long-distance communication. In the 3GPP Rel. 17 document, it is suggested that the above problems should be solved. This paper tries to solve the problem by proposing the two-step XGBOOST, a CART-based Gradient Boosting Model. Handover in TN uses measurement-based conditional handover (CHO), but the measured values in the NTN environment are not valid. Using this, the distance between the UE and the center of the cell and the elevation angle are used to construct a model that predicts the HO triggering time point. In order to overcome the propagation delay caused by communication at a high altitude, a model that predicts the distance and elevation angle between the UE and the center of the cell considering the propagation delay is proposed. The model is composed of two-step XGBOOST. The one-step model is a model in which the UE predicts the distance and elevation angle between cell centers after propagation delay at the time when satellite position information is transmitted to the UE. The two-step model predicts handover triggering occurrence based on the data predicted by the one-step result. As a result of the experiment, the model considering the propagation delay showed about 8% better performance on average than the model not considering the propagation delay, and the XGBOOST model achieved an average F1-score of 0.9891 in the propagation delay experiments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Optimization and Machine Learning for Wireless Communications)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle Pattern Shaping by Utilizing EBG Phase Response and Its Use in MIMO Radio Altimeter Antenna Design for Aircraft by Serap Kiriş, Serap Kiriş,  Fatih Özkan Alkurt and Fatih Özkan Alkurt and  Muharrem Karaaslan
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3434; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163434 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
In this study, a novel pattern shaping technique is presented and applied to the uniquely designed multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) radio altimeter antenna, acquiring area gain. Inspired by the behavior of the perfect electric conductor, the tendency to gather a diffuse pattern is exploited
[...] Read more.
In this study, a novel pattern shaping technique is presented and applied to the uniquely designed multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) radio altimeter antenna, acquiring area gain. Inspired by the behavior of the perfect electric conductor, the tendency to gather a diffuse pattern is exploited to create pattern shaping. A surface with a phase response of 0° at 3.824 GHz was designed to ensure that the target radio altimeter frequency of 4.3 GHz is in the immediate vicinity of the outer phase region, where the impedance is around 166.84 Ω, transforming the diffuse pattern of the top antenna into the target conical shape. Antenna reflection values are measured as −20.072 dB at 4.344 GHz (port 1) and −27.44 dB at 4.32 GHz (port 2), while there is 6 mm between the top antenna and its reflector. At 4.32 GHz, the envelope correlation coefficient is 0.0043, the diversity gain is 9.999, and the transmission value between the opposing ports is −29.08 dB, which indicates a low mutual coupling. A MIMO antenna with a measured gain of 10.1497 dBi for port 1 and 10.5617 dBi for port 2 conforming to the design criteria of the radio altimeter is achieved.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures Muharrem Karaaslan
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3434; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163434 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
In this study, a novel pattern shaping technique is presented and applied to the uniquely designed multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) radio altimeter antenna, acquiring area gain. Inspired by the behavior of the perfect electric conductor, the tendency to gather a diffuse pattern is exploited
[...] Read more.
In this study, a novel pattern shaping technique is presented and applied to the uniquely designed multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) radio altimeter antenna, acquiring area gain. Inspired by the behavior of the perfect electric conductor, the tendency to gather a diffuse pattern is exploited to create pattern shaping. A surface with a phase response of 0° at 3.824 GHz was designed to ensure that the target radio altimeter frequency of 4.3 GHz is in the immediate vicinity of the outer phase region, where the impedance is around 166.84 Ω, transforming the diffuse pattern of the top antenna into the target conical shape. Antenna reflection values are measured as −20.072 dB at 4.344 GHz (port 1) and −27.44 dB at 4.32 GHz (port 2), while there is 6 mm between the top antenna and its reflector. At 4.32 GHz, the envelope correlation coefficient is 0.0043, the diversity gain is 9.999, and the transmission value between the opposing ports is −29.08 dB, which indicates a low mutual coupling. A MIMO antenna with a measured gain of 10.1497 dBi for port 1 and 10.5617 dBi for port 2 conforming to the design criteria of the radio altimeter is achieved.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle Energy-Efficient Power Allocation for Full-Duplex Device-to-Device Underlaying Cellular Networks with NOMA by Xu Zhao, Xu Zhao,  Fang Liu, Fang Liu,  Yajing Zhang, Yajing Zhang,  Songchao Chen and Songchao Chen and  Jie Gan
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3433; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163433 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
Full-duplex (FD), Device-to-Device (D2D) and non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) are promising wireless communication techniques to improve the utilization of spectrum resources. Meanwhile, introducing FD, D2D and NOMA in cellular networks is very challenging due to the complex interference problem. To deal with the
[...] Read more.
Full-duplex (FD), Device-to-Device (D2D) and non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) are promising wireless communication techniques to improve the utilization of spectrum resources. Meanwhile, introducing FD, D2D and NOMA in cellular networks is very challenging due to the complex interference problem. To deal with the complex interference of FD D2D underlaying NOMA cellular networks, power allocation (PA) is extensively studied as an efficient interference management technique. However, most of the previous research works on PA to optimize energy efficiency only consider the system framework of partially joint combining techniques of FD, D2D and NOMA, and the constraints of optimization problem are very different. In this paper, in order to further improve the energy efficiency of a system, a dual-layer iteration power allocation algorithm is proposed to eliminate the complex interference. The outer-layer iteration is to solve the non-linear fractional objective function based on Dinkelbach, and the inner-layer iteration is to solve the non-convex optimization problem based on D.C. programming. Then, the non-convex and non-linear fractional objective function is transformed into a convex function to solve the optimal power allocation. In this approach, FD D2D users reuse the spectrum with downlink NOMA cellular users. Imperfect self-interference (SI) cancellation at the FD D2D users and the successive interference cancellation (SIC) at the strong NOMA user are considered in the system framework. The optimization problem is constructed to maximize the system’s energy efficiency with the constraints of successful SIC, QoS requirements, the maximum transmit power of BS and FD D2D users. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm outperforms the traditional orthogonal multiple access (OMA) in terms of energy efficiency with a higher system sum rate.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Broadband Wireless Transmission and Networks: Latest Advances and Prospects)
►▼
Show Figures Jie Gan
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3433; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163433 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
Full-duplex (FD), Device-to-Device (D2D) and non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) are promising wireless communication techniques to improve the utilization of spectrum resources. Meanwhile, introducing FD, D2D and NOMA in cellular networks is very challenging due to the complex interference problem. To deal with the
[...] Read more.
Full-duplex (FD), Device-to-Device (D2D) and non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) are promising wireless communication techniques to improve the utilization of spectrum resources. Meanwhile, introducing FD, D2D and NOMA in cellular networks is very challenging due to the complex interference problem. To deal with the complex interference of FD D2D underlaying NOMA cellular networks, power allocation (PA) is extensively studied as an efficient interference management technique. However, most of the previous research works on PA to optimize energy efficiency only consider the system framework of partially joint combining techniques of FD, D2D and NOMA, and the constraints of optimization problem are very different. In this paper, in order to further improve the energy efficiency of a system, a dual-layer iteration power allocation algorithm is proposed to eliminate the complex interference. The outer-layer iteration is to solve the non-linear fractional objective function based on Dinkelbach, and the inner-layer iteration is to solve the non-convex optimization problem based on D.C. programming. Then, the non-convex and non-linear fractional objective function is transformed into a convex function to solve the optimal power allocation. In this approach, FD D2D users reuse the spectrum with downlink NOMA cellular users. Imperfect self-interference (SI) cancellation at the FD D2D users and the successive interference cancellation (SIC) at the strong NOMA user are considered in the system framework. The optimization problem is constructed to maximize the system’s energy efficiency with the constraints of successful SIC, QoS requirements, the maximum transmit power of BS and FD D2D users. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm outperforms the traditional orthogonal multiple access (OMA) in terms of energy efficiency with a higher system sum rate.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Broadband Wireless Transmission and Networks: Latest Advances and Prospects)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle Research on Online Monitoring Method for Bond Wire Fatigue Applied to IGBT Module by Hongtao Liu, Hongtao Liu,  Fei Wang, Fei Wang,  Weiyi Xia and Weiyi Xia and  Chaoyue Shen
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3432; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163432 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
Bond wire fatigue is a prominent problem affecting the reliability of IGBT modules and power electronic converters, and has thus received much attention in the research community. As bond wire fatigue leads to changes in the gate circuit parameters, it affects the IGBT
[...] Read more.
Bond wire fatigue is a prominent problem affecting the reliability of IGBT modules and power electronic converters, and has thus received much attention in the research community. As bond wire fatigue leads to changes in the gate circuit parameters, it affects the IGBT turn-off process. Based on this finding, this paper proposes a fatigue evaluation method for bond wire based on IGBT turn-off time. This includes constructing a turn-off time-bond wire fatigue model that considers the impact of changes in collector current, and developing a control software that utilizes the coupling relationship between the Kelvin terminal voltage VeE and turn-off time for the online extraction of IGBT turn-off time. In summary, the proposed online monitoring method of IGBT bond wire fatigue based on turn-off time can help improve the reliability of power electronic converters.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures Chaoyue Shen
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3432; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163432 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
Bond wire fatigue is a prominent problem affecting the reliability of IGBT modules and power electronic converters, and has thus received much attention in the research community. As bond wire fatigue leads to changes in the gate circuit parameters, it affects the IGBT
[...] Read more.
Bond wire fatigue is a prominent problem affecting the reliability of IGBT modules and power electronic converters, and has thus received much attention in the research community. As bond wire fatigue leads to changes in the gate circuit parameters, it affects the IGBT turn-off process. Based on this finding, this paper proposes a fatigue evaluation method for bond wire based on IGBT turn-off time. This includes constructing a turn-off time-bond wire fatigue model that considers the impact of changes in collector current, and developing a control software that utilizes the coupling relationship between the Kelvin terminal voltage VeE and turn-off time for the online extraction of IGBT turn-off time. In summary, the proposed online monitoring method of IGBT bond wire fatigue based on turn-off time can help improve the reliability of power electronic converters.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle Ellipse Detection with Applications of Convolutional Neural Network in Industrial Images by Kang Liu, Kang Liu,  Yonggang Lu, Yonggang Lu,  Rubing Bai, Rubing Bai,  Kun Xu, Kun Xu,  Tao Peng, Tao Peng,  Yichun Tai and Yichun Tai and  Zhijiang Zhang
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3431; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163431 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
Ellipse detection has a very wide range of applications in the field of industrial production, especially in the geometric detection of metallurgical hinge pins. However, the factors in industrial images, such as small object size and incomplete ellipse in the image boundary, bring
[...] Read more.
Ellipse detection has a very wide range of applications in the field of industrial production, especially in the geometric detection of metallurgical hinge pins. However, the factors in industrial images, such as small object size and incomplete ellipse in the image boundary, bring challenges to ellipse detection, which cannot be solved by existing methods. This paper proposes a method for ellipse detection in industrial images, which utilizes the extended proposal operation to prevent the loss of ellipse rotation angle features during ellipse regression. Moreover, the Gaussian angle distance conforming to the ellipse axioms is adopted and combined with smooth L1 loss as the ellipse regression loss function to enhance the prediction accuracy of the ellipse rotation angle. The effectiveness of the proposed method is demonstrated on the hinge pins dataset, with experiment results showing an AP* of 80.93% and indicating superior detection performance compared to other methods. It is thus suitable for engineering applications and can provide visual guidance for the precise measurement of ellipse-like mechanical parts.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Detection, Recognition and Segmentation in Images and Videos)
►▼
Show Figures Zhijiang Zhang
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3431; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163431 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
Ellipse detection has a very wide range of applications in the field of industrial production, especially in the geometric detection of metallurgical hinge pins. However, the factors in industrial images, such as small object size and incomplete ellipse in the image boundary, bring
[...] Read more.
Ellipse detection has a very wide range of applications in the field of industrial production, especially in the geometric detection of metallurgical hinge pins. However, the factors in industrial images, such as small object size and incomplete ellipse in the image boundary, bring challenges to ellipse detection, which cannot be solved by existing methods. This paper proposes a method for ellipse detection in industrial images, which utilizes the extended proposal operation to prevent the loss of ellipse rotation angle features during ellipse regression. Moreover, the Gaussian angle distance conforming to the ellipse axioms is adopted and combined with smooth L1 loss as the ellipse regression loss function to enhance the prediction accuracy of the ellipse rotation angle. The effectiveness of the proposed method is demonstrated on the hinge pins dataset, with experiment results showing an AP* of 80.93% and indicating superior detection performance compared to other methods. It is thus suitable for engineering applications and can provide visual guidance for the precise measurement of ellipse-like mechanical parts.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Detection, Recognition and Segmentation in Images and Videos)
►▼
Show Figures
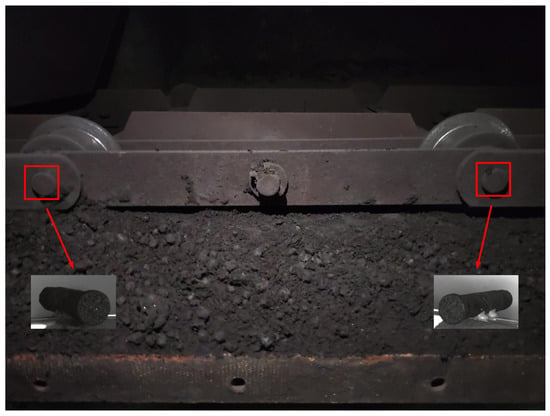 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle MHlinker: Research on a Joint Extraction Method of Fault Entity Relationship for Mine Hoist by Xiaochao Dang, Xiaochao Dang,  Han Deng, Han Deng,  Xiaohui Dong, Xiaohui Dong,  Zhongyan Zhu, Zhongyan Zhu,  Fenfang Li and Fenfang Li and  Li Wang
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3430; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163430 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
Triplet extraction is the key technology to automatically construct knowledge graphs. Extracting the triplet of mechanical equipment fault relationships is of great significance in constructing the fault diagnosis of a mine hoist. The pipeline triple extraction method will bring problems such as error
[...] Read more.
Triplet extraction is the key technology to automatically construct knowledge graphs. Extracting the triplet of mechanical equipment fault relationships is of great significance in constructing the fault diagnosis of a mine hoist. The pipeline triple extraction method will bring problems such as error accumulation and information redundancy. The existing joint learning methods cannot be applied to fault texts with more overlapping relationships, ignoring the particularity of professional knowledge in the field of complex mechanical equipment faults. Therefore, based on the Chinese pre-trained language model BERT Whole Word Masking (BERT-wwm), this paper proposes a joint entity and relation extraction model MHlinker (Mine Hoist linker, MHlinker) for the mine hoist fault field. This method uses BERT-wwm as the underlying encoder. In the entity recognition stage, the classification matrix is constructed using the multi-head extraction paradigm, which effectively solves the problem of entity nesting. The results show that this method enhances the model’s ability to extract fault relationships as a whole. When the small-scale manually labeled mine hoist fault text data set is tested, the extraction effect of entities and relationships is significantly improved compared with several baseline models.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Artificial Intelligence)
►▼
Show Figures Li Wang
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3430; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163430 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
Triplet extraction is the key technology to automatically construct knowledge graphs. Extracting the triplet of mechanical equipment fault relationships is of great significance in constructing the fault diagnosis of a mine hoist. The pipeline triple extraction method will bring problems such as error
[...] Read more.
Triplet extraction is the key technology to automatically construct knowledge graphs. Extracting the triplet of mechanical equipment fault relationships is of great significance in constructing the fault diagnosis of a mine hoist. The pipeline triple extraction method will bring problems such as error accumulation and information redundancy. The existing joint learning methods cannot be applied to fault texts with more overlapping relationships, ignoring the particularity of professional knowledge in the field of complex mechanical equipment faults. Therefore, based on the Chinese pre-trained language model BERT Whole Word Masking (BERT-wwm), this paper proposes a joint entity and relation extraction model MHlinker (Mine Hoist linker, MHlinker) for the mine hoist fault field. This method uses BERT-wwm as the underlying encoder. In the entity recognition stage, the classification matrix is constructed using the multi-head extraction paradigm, which effectively solves the problem of entity nesting. The results show that this method enhances the model’s ability to extract fault relationships as a whole. When the small-scale manually labeled mine hoist fault text data set is tested, the extraction effect of entities and relationships is significantly improved compared with several baseline models.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Artificial Intelligence)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle Hybrid Hunter–Prey Optimization with Deep Learning-Based Fintech for Predicting Financial Crises in the Economy and Society by Iyad Katib, Iyad Katib,  Fatmah Y. Assiri, Fatmah Y. Assiri,  Turki Althaqafi, Turki Althaqafi,  Zenah Mahmoud AlKubaisy, Zenah Mahmoud AlKubaisy,  Diaa Hamed and Diaa Hamed and  Mahmoud Ragab
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3429; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163429 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
Financial technology (Fintech) plays a pivotal role in driving contemporary technology, society, economies, and many other fields. The new-generation Fintech is Smart Fintech, mainly empowered and inspired by data science and artificial intelligence (DSAI) technologies. Smart Fintech combines DSAI and transforms finance and
[...] Read more.
Financial technology (Fintech) plays a pivotal role in driving contemporary technology, society, economies, and many other fields. The new-generation Fintech is Smart Fintech, mainly empowered and inspired by data science and artificial intelligence (DSAI) technologies. Smart Fintech combines DSAI and transforms finance and economies for driving automated, intelligent, personalized financial and economic businesses, services and systems, and the whole of business. The strength and growth of the country’s economy were evaluated with the accurate prediction of how many companies will succeed and how many will fail. Financial crisis prediction (FCP) has a considerable effect on the economy. Prior research focuses mainly on deep learning (DL), machine learning (ML), and statistical approaches for forecasting the financial health of a company. Thus, this study presents a hybrid hunter–prey optimization with a deep learning-based FCP (HHPODL-FCP) technique. The objective of the HHPODL-FCP algorithm lies in the effective identification of the financial crisis in enterprises or organizations. To accomplish this, the HHPODL-FCP method makes use of the HHPO algorithm for the feature subset selection process. In addition, the HHPODL-FCP technique employs the gated attention recurrent network (GARN) model for the identification and classification of financial and non-financial crises. The HHPODL-FCP method exploits a sparrow search algorithm (SSA)-based hyperparameter tuning process to enrich the performance of the GARN model. The simulation results of the HHPODL-FCP method are tested on different financial datasets. A wide range of experiments highlighted the remarkable performance of the HHPODL-FCP method over recent techniques under various measures.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Applications of Emerging Digital Technologies in Economy and Society)
►▼
Show Figures Mahmoud Ragab
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3429; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163429 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
Financial technology (Fintech) plays a pivotal role in driving contemporary technology, society, economies, and many other fields. The new-generation Fintech is Smart Fintech, mainly empowered and inspired by data science and artificial intelligence (DSAI) technologies. Smart Fintech combines DSAI and transforms finance and
[...] Read more.
Financial technology (Fintech) plays a pivotal role in driving contemporary technology, society, economies, and many other fields. The new-generation Fintech is Smart Fintech, mainly empowered and inspired by data science and artificial intelligence (DSAI) technologies. Smart Fintech combines DSAI and transforms finance and economies for driving automated, intelligent, personalized financial and economic businesses, services and systems, and the whole of business. The strength and growth of the country’s economy were evaluated with the accurate prediction of how many companies will succeed and how many will fail. Financial crisis prediction (FCP) has a considerable effect on the economy. Prior research focuses mainly on deep learning (DL), machine learning (ML), and statistical approaches for forecasting the financial health of a company. Thus, this study presents a hybrid hunter–prey optimization with a deep learning-based FCP (HHPODL-FCP) technique. The objective of the HHPODL-FCP algorithm lies in the effective identification of the financial crisis in enterprises or organizations. To accomplish this, the HHPODL-FCP method makes use of the HHPO algorithm for the feature subset selection process. In addition, the HHPODL-FCP technique employs the gated attention recurrent network (GARN) model for the identification and classification of financial and non-financial crises. The HHPODL-FCP method exploits a sparrow search algorithm (SSA)-based hyperparameter tuning process to enrich the performance of the GARN model. The simulation results of the HHPODL-FCP method are tested on different financial datasets. A wide range of experiments highlighted the remarkable performance of the HHPODL-FCP method over recent techniques under various measures.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Applications of Emerging Digital Technologies in Economy and Society)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle A Hierarchical Energy Control Strategy for Hybrid Electric Vehicle with Fuel Cell/Battery/Ultracapacitor Combining Fuzzy Controller and Status Regulator by Xiaorui Jia and Xiaorui Jia and  Mi Zhao
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3428; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163428 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
In order to improve the fuel economy of fuel cell hybrid electric vehicles (FCHEV), a hierarchical energy management strategy (HEMS) is proposed to rationally allocate the required power to a hybrid power system with three energy sources: fuel cell, battery, and ultracapacitor. First
[...] Read more.
In order to improve the fuel economy of fuel cell hybrid electric vehicles (FCHEV), a hierarchical energy management strategy (HEMS) is proposed to rationally allocate the required power to a hybrid power system with three energy sources: fuel cell, battery, and ultracapacitor. First of all, batteries and ultracapacitors are regarded as energy storage systems (ESS), which convert the distribution problem from three energy sources to two couples of energy sources. Secondly, fuzzy logic controllers are utilized in upper-layer energy management strategies (EMS) to distribute required power to fuel cell systems and the ESS. To extend the service life of the fuel cell and increase the maintenance ability of the state of charge (SOC) of the battery, a status regulation module is introduced to allocate the required power combined with fuzzy controller. Thirdly, an adaptive low-pass filter is applied to a lower-layer EMS based on the energy characteristics of the ultracapacitor, which fully utilizes the ultracapacitor. Finally, the economic and dynamic performance of the vehicle are compared between the HEMS and the power following strategy (PFS) under five typical cycle conditions: UDDS, WVUINTER, NEDC, HWFET and COMBINE. The results of the simulation show that the hydrogen consumption of the HEMS is reduced and the overall vehicle energy efficiency is increased in four operating conditions, which indicates that the proposed strategy has better economic performance. In addition, the dynamic performance of the vehicle is also improved.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Condition Monitoring and Diagnostic Methods for Power Equipment in New Energy Power Systems)
►▼
Show Figures Mi Zhao
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3428; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163428 (registering DOI) - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
In order to improve the fuel economy of fuel cell hybrid electric vehicles (FCHEV), a hierarchical energy management strategy (HEMS) is proposed to rationally allocate the required power to a hybrid power system with three energy sources: fuel cell, battery, and ultracapacitor. First
[...] Read more.
In order to improve the fuel economy of fuel cell hybrid electric vehicles (FCHEV), a hierarchical energy management strategy (HEMS) is proposed to rationally allocate the required power to a hybrid power system with three energy sources: fuel cell, battery, and ultracapacitor. First of all, batteries and ultracapacitors are regarded as energy storage systems (ESS), which convert the distribution problem from three energy sources to two couples of energy sources. Secondly, fuzzy logic controllers are utilized in upper-layer energy management strategies (EMS) to distribute required power to fuel cell systems and the ESS. To extend the service life of the fuel cell and increase the maintenance ability of the state of charge (SOC) of the battery, a status regulation module is introduced to allocate the required power combined with fuzzy controller. Thirdly, an adaptive low-pass filter is applied to a lower-layer EMS based on the energy characteristics of the ultracapacitor, which fully utilizes the ultracapacitor. Finally, the economic and dynamic performance of the vehicle are compared between the HEMS and the power following strategy (PFS) under five typical cycle conditions: UDDS, WVUINTER, NEDC, HWFET and COMBINE. The results of the simulation show that the hydrogen consumption of the HEMS is reduced and the overall vehicle energy efficiency is increased in four operating conditions, which indicates that the proposed strategy has better economic performance. In addition, the dynamic performance of the vehicle is also improved.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Condition Monitoring and Diagnostic Methods for Power Equipment in New Energy Power Systems)
►▼
Show Figures
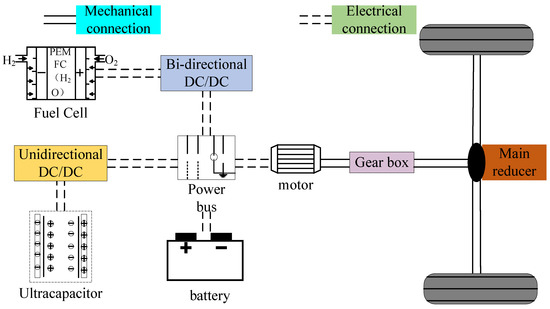 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle Field Programmable Analog Array Based Non-Integer Filter Designs by Alexandros Pagidas, Alexandros Pagidas,  Costas Psychalinos and Costas Psychalinos and  Ahmed S. Elwakil
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3427; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163427 (registering DOI) - 13 Aug 2023
Abstract
The approximation of the frequency behavior of fractional-order, power-law, and double-order filters can be performed by the same rational integer-order transfer function. This can be achieved through the utilization of a curve fitting based approximation. Moreover, their implementation can be performed by the
[...] Read more.
The approximation of the frequency behavior of fractional-order, power-law, and double-order filters can be performed by the same rational integer-order transfer function. This can be achieved through the utilization of a curve fitting based approximation. Moreover, their implementation can be performed by the same core, by only changing the corresponding time constants and scaling factors. The aforementioned findings are experimentally verified using a Field Programmable Analog Array device.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Advanced Design Techniques and EDA Methodologies for Analog, RF and MM-Wave Circuit Design)
►▼
Show Figures Ahmed S. Elwakil
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3427; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163427 (registering DOI) - 13 Aug 2023
Abstract
The approximation of the frequency behavior of fractional-order, power-law, and double-order filters can be performed by the same rational integer-order transfer function. This can be achieved through the utilization of a curve fitting based approximation. Moreover, their implementation can be performed by the
[...] Read more.
The approximation of the frequency behavior of fractional-order, power-law, and double-order filters can be performed by the same rational integer-order transfer function. This can be achieved through the utilization of a curve fitting based approximation. Moreover, their implementation can be performed by the same core, by only changing the corresponding time constants and scaling factors. The aforementioned findings are experimentally verified using a Field Programmable Analog Array device.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Advanced Design Techniques and EDA Methodologies for Analog, RF and MM-Wave Circuit Design)
►▼
Show Figures
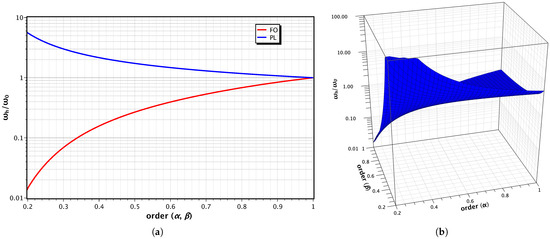 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle Intelligent Mesh Cluster Algorithm for Device-Free Localization in Wireless Sensor Networks by Chao Sun, Chao Sun,  Junhao Zhou, Junhao Zhou,  Kyong-Seok Jang and Kyong-Seok Jang and  Youngok Kim
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3426; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163426 (registering DOI) - 13 Aug 2023
Abstract
Device-free localization (DFL) is a technology designed to determine the positions of targets without the need for them to carry electronic devices. It achieves this by analyzing the shadowing effects of radio links within wireless sensor networks (WSNs). However, obtaining high precision in
[...] Read more.
Device-free localization (DFL) is a technology designed to determine the positions of targets without the need for them to carry electronic devices. It achieves this by analyzing the shadowing effects of radio links within wireless sensor networks (WSNs). However, obtaining high precision in DFL often results in increased energy consumption, severe electromagnetic interference, and other challenges that impact positioning accuracy. Most DFL schemes for accurate tracking require substantial memory and computing resources, which make them unsuitable for resource-constrained applications. To address these challenges, we propose an intelligent mesh cluster (IMC) algorithm that achieves accurate tracking by adaptively activating a subset of wireless links. This approach not only reduces electromagnetic interference but also saves energy. The IMC algorithm leverages geometric objects, such as meshes and mesh clusters formed by wireless links, to achieve low computational complexity. By scanning a subset of mesh cluster-related wireless links near the DFL target, the algorithm significantly reduces the computational requirements. The target’s location estimate is determined based on the connection information among the mesh clusters. We conducted numerous simulations to evaluate the performance of the IMC algorithm. The results demonstrate that the IMC algorithm outperforms grid-based and particle filter-based DFL methods, confirming its effectiveness in achieving accurate and efficient localization.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Communication and Networking Techniques for Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT))
►▼
Show Figures Youngok Kim
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3426; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163426 (registering DOI) - 13 Aug 2023
Abstract
Device-free localization (DFL) is a technology designed to determine the positions of targets without the need for them to carry electronic devices. It achieves this by analyzing the shadowing effects of radio links within wireless sensor networks (WSNs). However, obtaining high precision in
[...] Read more.
Device-free localization (DFL) is a technology designed to determine the positions of targets without the need for them to carry electronic devices. It achieves this by analyzing the shadowing effects of radio links within wireless sensor networks (WSNs). However, obtaining high precision in DFL often results in increased energy consumption, severe electromagnetic interference, and other challenges that impact positioning accuracy. Most DFL schemes for accurate tracking require substantial memory and computing resources, which make them unsuitable for resource-constrained applications. To address these challenges, we propose an intelligent mesh cluster (IMC) algorithm that achieves accurate tracking by adaptively activating a subset of wireless links. This approach not only reduces electromagnetic interference but also saves energy. The IMC algorithm leverages geometric objects, such as meshes and mesh clusters formed by wireless links, to achieve low computational complexity. By scanning a subset of mesh cluster-related wireless links near the DFL target, the algorithm significantly reduces the computational requirements. The target’s location estimate is determined based on the connection information among the mesh clusters. We conducted numerous simulations to evaluate the performance of the IMC algorithm. The results demonstrate that the IMC algorithm outperforms grid-based and particle filter-based DFL methods, confirming its effectiveness in achieving accurate and efficient localization.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Communication and Networking Techniques for Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT))
►▼
Show Figures
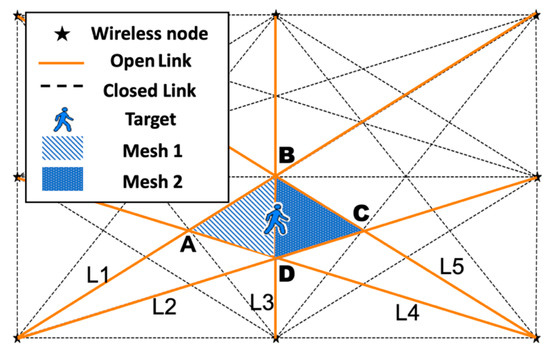 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle A CNN-Based Adaptive Federated Learning Approach for Communication Jamming Recognition by Ningsong Zhang, Ningsong Zhang,  Yusheng Li, Yusheng Li,  Yuxin Shi and Yuxin Shi and  Junren Shen
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3425; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163425 (registering DOI) - 13 Aug 2023
Abstract
The effective and accurate recognition of communication jamming is crucial for enhancing the anti-jamming capability of wireless communication systems. At present, a significant portion of jamming data is decentralized, stored in local nodes, and cannot be uploaded directly for network training due to
[...] Read more.
The effective and accurate recognition of communication jamming is crucial for enhancing the anti-jamming capability of wireless communication systems. At present, a significant portion of jamming data is decentralized, stored in local nodes, and cannot be uploaded directly for network training due to its sensitive nature. To address this challenge, we introduce a novel distributed jamming recognition method. This method leverages a distributed recognition framework to achieve global optimization through federated learning. Each node independently trains its local model and contributes to the comprehensive global model. We have devised an adaptive adjustment mechanism for the mixed weight parameters of both local and global models, ensuring an automatic balance between the global model and the aggregated insights from local data across devices. Simulations indicate that our personalization strategy yields a 30% boost in accuracy, and the adaptive weight parameters further enhance the recognition accuracy by 1.1%.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Multi-Scale Communications and Signal Processing)
get_app
Open AccessArticle
Application of Improved Butterfly Optimization Algorithm in Mobile Robot Path Planning
by Junren Shen
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3425; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163425 (registering DOI) - 13 Aug 2023
Abstract
The effective and accurate recognition of communication jamming is crucial for enhancing the anti-jamming capability of wireless communication systems. At present, a significant portion of jamming data is decentralized, stored in local nodes, and cannot be uploaded directly for network training due to
[...] Read more.
The effective and accurate recognition of communication jamming is crucial for enhancing the anti-jamming capability of wireless communication systems. At present, a significant portion of jamming data is decentralized, stored in local nodes, and cannot be uploaded directly for network training due to its sensitive nature. To address this challenge, we introduce a novel distributed jamming recognition method. This method leverages a distributed recognition framework to achieve global optimization through federated learning. Each node independently trains its local model and contributes to the comprehensive global model. We have devised an adaptive adjustment mechanism for the mixed weight parameters of both local and global models, ensuring an automatic balance between the global model and the aggregated insights from local data across devices. Simulations indicate that our personalization strategy yields a 30% boost in accuracy, and the adaptive weight parameters further enhance the recognition accuracy by 1.1%.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Multi-Scale Communications and Signal Processing)
get_app
Open AccessArticle
Application of Improved Butterfly Optimization Algorithm in Mobile Robot Path Planning
by
 Rongjie Zhai, Rongjie Zhai,  Ping Xiao, Ping Xiao,  Da Shu, Da Shu,  Yongjiu Sun and Yongjiu Sun and  Min Jiang
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3424; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163424 (registering DOI) - 13 Aug 2023
Abstract
An improved butterfly optimization algorithm (IBOA) is proposed to overcome the disadvantages, including slow convergence, generation of local optimum solutions, and deadlock phenomenon, of the optimization algorithm in the path planning of mobile robots. A path-planning grid model is established based on an
[...] Read more.
An improved butterfly optimization algorithm (IBOA) is proposed to overcome the disadvantages, including slow convergence, generation of local optimum solutions, and deadlock phenomenon, of the optimization algorithm in the path planning of mobile robots. A path-planning grid model is established based on an improved obstacle model. First, the population diversity is improved by introducing kent mapping during population position renewal in the normal butterfly optimization algorithm (BOA) to enhance the global search ability of the butterfly population. Second, an adaptive weight coefficient is introduced in the renewal process of each generation to increase the convergence speed and accuracy. An opposition-based learning strategy based on convex lens imaging is introduced to help the butterfly population jump out of the local optimum. Finally, a mutation strategy is introduced to solve the path planning problem. On this basis, two path simplification strategies are proposed to make up for the shortcomings of planning paths in grid maps. The shortest path lengths solved by IBOA, BOA, and GA in the 20 × 20 map are 30.97, 31.799, and 31.799, respectively. The numbers of iterations for the shortest paths searched by IBOA, BOA, and GA are 14, 24, and 38 in that order. The shortest path lengths solved by IBOA, BOA and GA in the 40 × 40 map are 63.84, 65.60, and 65.84, respectively. The number of iterations for the shortest paths searched by IBOA, BOA and GA are 32, 40, and 46, respectively. Simulation results show that IBOA has a strong ability to solve robot path planning problems and that the proposed path simplification strategy can effectively reduce the length of the optimal path in the grid map to solve the path planning problem of mobile robots. The shortest paths solved by IBOA in 20 × 20 and 40 × 40 maps are simplified to lengths of 30.2914 and 61.03, respectively.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue AI in Mobile Robotics)
►▼
Show Figures Min Jiang
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3424; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163424 (registering DOI) - 13 Aug 2023
Abstract
An improved butterfly optimization algorithm (IBOA) is proposed to overcome the disadvantages, including slow convergence, generation of local optimum solutions, and deadlock phenomenon, of the optimization algorithm in the path planning of mobile robots. A path-planning grid model is established based on an
[...] Read more.
An improved butterfly optimization algorithm (IBOA) is proposed to overcome the disadvantages, including slow convergence, generation of local optimum solutions, and deadlock phenomenon, of the optimization algorithm in the path planning of mobile robots. A path-planning grid model is established based on an improved obstacle model. First, the population diversity is improved by introducing kent mapping during population position renewal in the normal butterfly optimization algorithm (BOA) to enhance the global search ability of the butterfly population. Second, an adaptive weight coefficient is introduced in the renewal process of each generation to increase the convergence speed and accuracy. An opposition-based learning strategy based on convex lens imaging is introduced to help the butterfly population jump out of the local optimum. Finally, a mutation strategy is introduced to solve the path planning problem. On this basis, two path simplification strategies are proposed to make up for the shortcomings of planning paths in grid maps. The shortest path lengths solved by IBOA, BOA, and GA in the 20 × 20 map are 30.97, 31.799, and 31.799, respectively. The numbers of iterations for the shortest paths searched by IBOA, BOA, and GA are 14, 24, and 38 in that order. The shortest path lengths solved by IBOA, BOA and GA in the 40 × 40 map are 63.84, 65.60, and 65.84, respectively. The number of iterations for the shortest paths searched by IBOA, BOA and GA are 32, 40, and 46, respectively. Simulation results show that IBOA has a strong ability to solve robot path planning problems and that the proposed path simplification strategy can effectively reduce the length of the optimal path in the grid map to solve the path planning problem of mobile robots. The shortest paths solved by IBOA in 20 × 20 and 40 × 40 maps are simplified to lengths of 30.2914 and 61.03, respectively.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue AI in Mobile Robotics)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle A Deep Learning-Enhanced Multi-Modal Sensing Platform for Robust Human Object Detection and Tracking in Challenging Environments by Peng Cheng, Peng Cheng,  Zinan Xiong, Zinan Xiong,  Yajie Bao, Yajie Bao,  Ping Zhuang, Ping Zhuang,  Yunqi Zhang, Yunqi Zhang,  Erik Blasch and Erik Blasch and  Genshe Chen
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3423; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163423 (registering DOI) - 12 Aug 2023
Abstract
In modern security situations, tracking multiple human objects in real-time within challenging urban environments is a critical capability for enhancing situational awareness, minimizing response time, and increasing overall operational effectiveness. Tracking multiple entities enables informed decision-making, risk mitigation, and the safeguarding of civil-military
[...] Read more.
In modern security situations, tracking multiple human objects in real-time within challenging urban environments is a critical capability for enhancing situational awareness, minimizing response time, and increasing overall operational effectiveness. Tracking multiple entities enables informed decision-making, risk mitigation, and the safeguarding of civil-military operations to ensure safety and mission success. This paper presents a multi-modal electro-optical/infrared (EO/IR) and radio frequency (RF) fused sensing (MEIRFS) platform for real-time human object detection, recognition, classification, and tracking in challenging environments. By utilizing different sensors in a complementary manner, the robustness of the sensing system is enhanced, enabling reliable detection and recognition results across various situations. Specifically designed radar tags and thermal tags can be used to discriminate between friendly and non-friendly objects. The system incorporates deep learning-based image fusion and human object recognition and tracking (HORT) algorithms to ensure accurate situation assessment. After integrating into an all-terrain robot, multiple ground tests were conducted to verify the consistency of the HORT in various environments. The MEIRFS sensor system has been designed to meet the Size, Weight, Power, and Cost (SWaP-C) requirements for installation on autonomous ground and aerial vehicles.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Multimodal Data Fusion and Computational Optimization for Intelligent Perception)
►▼
Show Figures Genshe Chen
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3423; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163423 (registering DOI) - 12 Aug 2023
Abstract
In modern security situations, tracking multiple human objects in real-time within challenging urban environments is a critical capability for enhancing situational awareness, minimizing response time, and increasing overall operational effectiveness. Tracking multiple entities enables informed decision-making, risk mitigation, and the safeguarding of civil-military
[...] Read more.
In modern security situations, tracking multiple human objects in real-time within challenging urban environments is a critical capability for enhancing situational awareness, minimizing response time, and increasing overall operational effectiveness. Tracking multiple entities enables informed decision-making, risk mitigation, and the safeguarding of civil-military operations to ensure safety and mission success. This paper presents a multi-modal electro-optical/infrared (EO/IR) and radio frequency (RF) fused sensing (MEIRFS) platform for real-time human object detection, recognition, classification, and tracking in challenging environments. By utilizing different sensors in a complementary manner, the robustness of the sensing system is enhanced, enabling reliable detection and recognition results across various situations. Specifically designed radar tags and thermal tags can be used to discriminate between friendly and non-friendly objects. The system incorporates deep learning-based image fusion and human object recognition and tracking (HORT) algorithms to ensure accurate situation assessment. After integrating into an all-terrain robot, multiple ground tests were conducted to verify the consistency of the HORT in various environments. The MEIRFS sensor system has been designed to meet the Size, Weight, Power, and Cost (SWaP-C) requirements for installation on autonomous ground and aerial vehicles.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Multimodal Data Fusion and Computational Optimization for Intelligent Perception)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle Identifying Users and Developers of Mobile Apps in Social Network Crowd by Ghadah Alamer, Ghadah Alamer,  Sultan Alyahya and Sultan Alyahya and  Hmood Al-Dossari
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3422; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163422 (registering DOI) - 12 Aug 2023
Abstract
In the last fifteen years, an immense expansion has been witnessed in mobile app usage and production. The intense competition in the tech sector and also the rapidly and constantly evolving user requirements have led to increased burden on mobile app creators. Nowadays,
[...] Read more.
In the last fifteen years, an immense expansion has been witnessed in mobile app usage and production. The intense competition in the tech sector and also the rapidly and constantly evolving user requirements have led to increased burden on mobile app creators. Nowadays, fulfilling users’ expectations cannot be readily achieved and new and unconventional approaches are needed to permit an interested crowd of users to contribute in the introduction of creative mobile apps. Indeed, users and developers of mobile apps are the most influential candidates to engage in any of the requirements engineering activities. The place where both can best be found is on Twitter, one of the most widely used social media platforms. More interestingly, Twitter is considered as a fertile ground for textual content generated by the crowd that can assist in building robust predictive classification models using machine learning (ML) and natural language processing (NLP) techniques. Therefore, in this study, we have built two classification models that can identify mobile apps users and developers using tweets. A thorough empirical comparison of different feature extraction techniques and machine learning classification algorithms were experimented with to find the best-performing mobile app user and developer classifiers. The results revealed that for mobile app user classification, the highest accuracy achieved was ≈0.86, produced via logistic regression (LR) using Term Frequency Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF) with N-gram (unigram, bigram and trigram), and the highest precision was ≈0.86, produced via LR using Bag-of-Words (BOW) with N-gram (unigram and bigram). On the other hand, for mobile app developer classification, the highest accuracy achieved was ≈0.87, produced by random forest (RF) using BOW with N-gram (unigram and bigram), and the highest precision was ≈0.88, produced by multi-layer perception neural network (MLP NN) using BERTweet for feature extraction. According to the results, we believe that the developed classification models are efficient and can assist in identifying mobile app users and developers from tweets. Moreover, we envision that our models can be harnessed as a crowd selection approach for crowdsourcing requirements engineering activities to enhance and design inventive and satisfying mobile apps.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Machine Learning (ML) and Software Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures Hmood Al-Dossari
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3422; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163422 (registering DOI) - 12 Aug 2023
Abstract
In the last fifteen years, an immense expansion has been witnessed in mobile app usage and production. The intense competition in the tech sector and also the rapidly and constantly evolving user requirements have led to increased burden on mobile app creators. Nowadays,
[...] Read more.
In the last fifteen years, an immense expansion has been witnessed in mobile app usage and production. The intense competition in the tech sector and also the rapidly and constantly evolving user requirements have led to increased burden on mobile app creators. Nowadays, fulfilling users’ expectations cannot be readily achieved and new and unconventional approaches are needed to permit an interested crowd of users to contribute in the introduction of creative mobile apps. Indeed, users and developers of mobile apps are the most influential candidates to engage in any of the requirements engineering activities. The place where both can best be found is on Twitter, one of the most widely used social media platforms. More interestingly, Twitter is considered as a fertile ground for textual content generated by the crowd that can assist in building robust predictive classification models using machine learning (ML) and natural language processing (NLP) techniques. Therefore, in this study, we have built two classification models that can identify mobile apps users and developers using tweets. A thorough empirical comparison of different feature extraction techniques and machine learning classification algorithms were experimented with to find the best-performing mobile app user and developer classifiers. The results revealed that for mobile app user classification, the highest accuracy achieved was ≈0.86, produced via logistic regression (LR) using Term Frequency Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF) with N-gram (unigram, bigram and trigram), and the highest precision was ≈0.86, produced via LR using Bag-of-Words (BOW) with N-gram (unigram and bigram). On the other hand, for mobile app developer classification, the highest accuracy achieved was ≈0.87, produced by random forest (RF) using BOW with N-gram (unigram and bigram), and the highest precision was ≈0.88, produced by multi-layer perception neural network (MLP NN) using BERTweet for feature extraction. According to the results, we believe that the developed classification models are efficient and can assist in identifying mobile app users and developers from tweets. Moreover, we envision that our models can be harnessed as a crowd selection approach for crowdsourcing requirements engineering activities to enhance and design inventive and satisfying mobile apps.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Machine Learning (ML) and Software Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle Improved Traffic Small Object Detection via Cross-Layer Feature Fusion and Channel Attention by Qinliang Chuai, Qinliang Chuai,  Xiaowei He and Xiaowei He and  Yi Li
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3421; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163421 (registering DOI) - 12 Aug 2023
Abstract
Small object detection has long been one of the most formidable challenges in computer vision due to the poor visual features and high noise of surroundings behind them. However, small targets in traffic scenes encompass a multitude of complex visual interfering factors, bearing
[...] Read more.
Small object detection has long been one of the most formidable challenges in computer vision due to the poor visual features and high noise of surroundings behind them. However, small targets in traffic scenes encompass a multitude of complex visual interfering factors, bearing crucial information such as traffic signs, traffic lights, and pedestrians. Given the inherent difficulties faced by generic models in addressing these issues, we conduct a comprehensive investigation on small target detection in this application scenario. In this work, we present a Cross-Layer Feature Fusion and Channel Attention algorithm based on a lightweight YOLOv5s design for traffic small target detection, named CFA-YOLO. To enhance the sensitivity of the model toward vital features, we embed the channel-guided Squeeze-and-Excitation (SE) block in the deep layer of the backbone. Moreover, the most excellent innovation of our work belongs to the effective cross-layer feature fusion method, which maintains robust feature fusion and information interaction capabilities; in addition, it simplifies redundant parameters compared with the baseline model. To align with the output features of the neck network, we adjusted the detection heads from three to two. Furthermore, we also applied the decoupled detection head for classification and bounding box regression tasks, respectively. This approach not only achieves real-time detection standards, but also improves the overall training results in parameter-friendly manner. The CFA-YOLO model significantly pays a lot of attention to the detail features of small targets, thereby it also has a great advantage in addressing the issue of poor performance in traffic small target detection results. Vast experiments have validated the efficiency and effectiveness of our proposed method in traffic small object detection. Compared with the latest lightweight detectors, such as YOLOv7-Tiny and YOLOv8s, our method consistently achieves superior performance both in terms of the model’s accuracy and complexity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Computer Vision and Image Processing)
►▼
Show Figures Yi Li
Electronics 2023, 12(16), 3421; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163421 (registering DOI) - 12 Aug 2023
Abstract
Small object detection has long been one of the most formidable challenges in computer vision due to the poor visual features and high noise of surroundings behind them. However, small targets in traffic scenes encompass a multitude of complex visual interfering factors, bearing
[...] Read more.
Small object detection has long been one of the most formidable challenges in computer vision due to the poor visual features and high noise of surroundings behind them. However, small targets in traffic scenes encompass a multitude of complex visual interfering factors, bearing crucial information such as traffic signs, traffic lights, and pedestrians. Given the inherent difficulties faced by generic models in addressing these issues, we conduct a comprehensive investigation on small target detection in this application scenario. In this work, we present a Cross-Layer Feature Fusion and Channel Attention algorithm based on a lightweight YOLOv5s design for traffic small target detection, named CFA-YOLO. To enhance the sensitivity of the model toward vital features, we embed the channel-guided Squeeze-and-Excitation (SE) block in the deep layer of the backbone. Moreover, the most excellent innovation of our work belongs to the effective cross-layer feature fusion method, which maintains robust feature fusion and information interaction capabilities; in addition, it simplifies redundant parameters compared with the baseline model. To align with the output features of the neck network, we adjusted the detection heads from three to two. Furthermore, we also applied the decoupled detection head for classification and bounding box regression tasks, respectively. This approach not only achieves real-time detection standards, but also improves the overall training results in parameter-friendly manner. The CFA-YOLO model significantly pays a lot of attention to the detail features of small targets, thereby it also has a great advantage in addressing the issue of poor performance in traffic small target detection results. Vast experiments have validated the efficiency and effectiveness of our proposed method in traffic small object detection. Compared with the latest lightweight detectors, such as YOLOv7-Tiny and YOLOv8s, our method consistently achieves superior performance both in terms of the model’s accuracy and complexity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Computer Vision and Image Processing)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 More Articles... Submit to Electronics
Review for Electronics
Share
Journal Menu
►
▼
Journal Menu
Electronics Home
Aims & Scope
Editorial Board
Reviewer Board
Topical Advisory Panel
Instructions for Authors
Special Issues
Topics
Sections & Collections
Article Processing Charge
Indexing & Archiving
Editor’s Choice Articles
Most Cited & Viewed
Journal Statistics
Journal History
Journal Awards
Society Collaborations
Conferences
Editorial Office
Journal Browser
►
▼
Journal Browser
arrow_forward_ios
Forthcoming issue
arrow_forward_ios
Current issue
Vol. 12 (2023)
Vol. 11 (2022)
Vol. 10 (2021)
Vol. 9 (2020)
Vol. 8 (2019)
Vol. 7 (2018)
Vol. 6 (2017)
Vol. 5 (2016)
Vol. 4 (2015)
Vol. 3 (2014)
Vol. 2 (2013)
Vol. 1 (2012)
Highly Accessed Articles
View More...
Latest Books
Submit to Electronics
Review for Electronics
Share
Journal Menu
►
▼
Journal Menu
Electronics Home
Aims & Scope
Editorial Board
Reviewer Board
Topical Advisory Panel
Instructions for Authors
Special Issues
Topics
Sections & Collections
Article Processing Charge
Indexing & Archiving
Editor’s Choice Articles
Most Cited & Viewed
Journal Statistics
Journal History
Journal Awards
Society Collaborations
Conferences
Editorial Office
Journal Browser
►
▼
Journal Browser
arrow_forward_ios
Forthcoming issue
arrow_forward_ios
Current issue
Vol. 12 (2023)
Vol. 11 (2022)
Vol. 10 (2021)
Vol. 9 (2020)
Vol. 8 (2019)
Vol. 7 (2018)
Vol. 6 (2017)
Vol. 5 (2016)
Vol. 4 (2015)
Vol. 3 (2014)
Vol. 2 (2013)
Vol. 1 (2012)
Highly Accessed Articles
View More...
Latest Books
 More Books and Reprints...
E-Mail Alert
News
11 August 2023
Electronics | Issue Cover Articles in 2022
11 August 2023
Meet Us at the 6th International Conference on Perovskite Solar Cell and Optoelectronics (PSCO 2023), 18–20 September 2023, Oxford, UK
More Books and Reprints...
E-Mail Alert
News
11 August 2023
Electronics | Issue Cover Articles in 2022
11 August 2023
Meet Us at the 6th International Conference on Perovskite Solar Cell and Optoelectronics (PSCO 2023), 18–20 September 2023, Oxford, UK
 27 July 2023
MDPI Insights: The CEO’s Letter #2
More News & Announcements...
Topics
Edit a Topic
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Electronics, Healthcare, JSAN, Sensors
Intelligent Health Monitoring and Assistance Systems and Frameworks
Topic Editors: Ismaeel Al Ridhawi, Ali KarimeDeadline: 20 August 2023
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Computers, Digital, Electronics, Smart Cities
Artificial Intelligence Models, Tools and Applications
Topic Editors: Phivos Mylonas, Katia Lida Kermanidis, Manolis MaragoudakisDeadline: 31 August 2023
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Energies, Mathematics, Electronics, Algorithms
Distributed Optimization for Control
Topic Editors: Honglei Xu, Lingyun WangDeadline: 20 September 2023
Topic in
Energies, Applied Sciences, Sensors, Electronics, Sci
Modeling and Optimizing Operation of Energy Internet
Topic Editors: Qiuye Sun, Rui Wang, Lei LiuDeadline: 30 September 2023
More Topics
27 July 2023
MDPI Insights: The CEO’s Letter #2
More News & Announcements...
Topics
Edit a Topic
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Electronics, Healthcare, JSAN, Sensors
Intelligent Health Monitoring and Assistance Systems and Frameworks
Topic Editors: Ismaeel Al Ridhawi, Ali KarimeDeadline: 20 August 2023
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Computers, Digital, Electronics, Smart Cities
Artificial Intelligence Models, Tools and Applications
Topic Editors: Phivos Mylonas, Katia Lida Kermanidis, Manolis MaragoudakisDeadline: 31 August 2023
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Energies, Mathematics, Electronics, Algorithms
Distributed Optimization for Control
Topic Editors: Honglei Xu, Lingyun WangDeadline: 20 September 2023
Topic in
Energies, Applied Sciences, Sensors, Electronics, Sci
Modeling and Optimizing Operation of Energy Internet
Topic Editors: Qiuye Sun, Rui Wang, Lei LiuDeadline: 30 September 2023
More Topics
 Conferences
Announce Your Conference
27 October–10 November 2023
The 4th International Electronic Conference on Applied Sciences (ASEC2023)
Conferences
Announce Your Conference
27 October–10 November 2023
The 4th International Electronic Conference on Applied Sciences (ASEC2023) 23–25 August 2023
The 2nd International Conference on Maritime IT Convergence
23–25 August 2023
The 2nd International Conference on Maritime IT Convergence 27–30 August 2023
International Conference on Functional Nanomaterials and Nanodevices 2023 (NANOMAT2023)
27–30 August 2023
International Conference on Functional Nanomaterials and Nanodevices 2023 (NANOMAT2023) More Conferences...
Special Issues
Edit a Special Issue
Special Issue in
Electronics
Recent Advances in Motion Planning and Control of Autonomous Vehicles
Guest Editors: Bai Li, Youmin Zhang, Xiaohui Li, Tankut AcarmanDeadline: 20 August 2023
Special Issue in
Electronics
Electronic Solutions for Artificial Intelligence Healthcare Volume II
Guest Editor: Jun-Ho HuhDeadline: 31 August 2023
Special Issue in
Electronics
Supercapacitor Applications
Guest Editor: Nihal KularatnaDeadline: 15 September 2023
Special Issue in
Electronics
Dependability of Emerging Computing Paradigms and Technologies in IoT-Oriented Circuits, Architectures and Algorithms
Guest Editors: Marcello Traiola, Elena-Ioana Vǎtǎjelu, Angeliki KritikakouDeadline: 30 September 2023
More Special Issues
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Electronics
Application of Advanced Computing, Control and Processing in Engineering
Collection Editors: Sudip Chakraborty, Robertas Damaševičius, Sergio Greco
Topical Collection in
Electronics
Instrumentation, Noise, Reliability
Collection Editor: Graziella Scandurra
Topical Collection in
Electronics
New Technologies for Biomedical Circuits and Systems
Collection Editors: S. Abdollah Mirbozorgi, Nima TaheriNejad
Topical Collection in
Electronics
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Techniques
Collection Editor: Donghyeon Cho
More Topical Collections
Electronics,
EISSN 2079-9292,
Published by MDPI
RSS
Content Alert
Further Information
Article Processing Charges
Pay an Invoice
Open Access Policy
Contact MDPI
Jobs at MDPI
Guidelines
For Authors
For Reviewers
For Editors
For Librarians
For Publishers
For Societies
For Conference Organizers
MDPI Initiatives
Sciforum
MDPI Books
Preprints.org
Scilit
SciProfiles
Encyclopedia
JAMS
Proceedings Series
Follow MDPI
LinkedIn
Facebook
Twitter
More Conferences...
Special Issues
Edit a Special Issue
Special Issue in
Electronics
Recent Advances in Motion Planning and Control of Autonomous Vehicles
Guest Editors: Bai Li, Youmin Zhang, Xiaohui Li, Tankut AcarmanDeadline: 20 August 2023
Special Issue in
Electronics
Electronic Solutions for Artificial Intelligence Healthcare Volume II
Guest Editor: Jun-Ho HuhDeadline: 31 August 2023
Special Issue in
Electronics
Supercapacitor Applications
Guest Editor: Nihal KularatnaDeadline: 15 September 2023
Special Issue in
Electronics
Dependability of Emerging Computing Paradigms and Technologies in IoT-Oriented Circuits, Architectures and Algorithms
Guest Editors: Marcello Traiola, Elena-Ioana Vǎtǎjelu, Angeliki KritikakouDeadline: 30 September 2023
More Special Issues
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Electronics
Application of Advanced Computing, Control and Processing in Engineering
Collection Editors: Sudip Chakraborty, Robertas Damaševičius, Sergio Greco
Topical Collection in
Electronics
Instrumentation, Noise, Reliability
Collection Editor: Graziella Scandurra
Topical Collection in
Electronics
New Technologies for Biomedical Circuits and Systems
Collection Editors: S. Abdollah Mirbozorgi, Nima TaheriNejad
Topical Collection in
Electronics
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Techniques
Collection Editor: Donghyeon Cho
More Topical Collections
Electronics,
EISSN 2079-9292,
Published by MDPI
RSS
Content Alert
Further Information
Article Processing Charges
Pay an Invoice
Open Access Policy
Contact MDPI
Jobs at MDPI
Guidelines
For Authors
For Reviewers
For Editors
For Librarians
For Publishers
For Societies
For Conference Organizers
MDPI Initiatives
Sciforum
MDPI Books
Preprints.org
Scilit
SciProfiles
Encyclopedia
JAMS
Proceedings Series
Follow MDPI
LinkedIn
Facebook
Twitter
 © 1996-2023 MDPI (Basel, Switzerland) unless otherwise stated
Disclaimer
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely
those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or
the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas,
methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
Terms and Conditions
Privacy Policy
We use cookies on our website to ensure you get the best experience.
Read more about our cookies here.
Accept
Share Link
Copy
clear
Share
https://www.mdpi.com/journal/electronics
clear
Back to TopTop
© 1996-2023 MDPI (Basel, Switzerland) unless otherwise stated
Disclaimer
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely
those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or
the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas,
methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
Terms and Conditions
Privacy Policy
We use cookies on our website to ensure you get the best experience.
Read more about our cookies here.
Accept
Share Link
Copy
clear
Share
https://www.mdpi.com/journal/electronics
clear
Back to TopTop
|
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |